1940’s
1946: Moldmaker Gil Carlson founds Caco, Inc. in Pomona, CA. and begins Apprenticeship Program. Fortune 100 corporations seek out Caco for multi-cavity molds with cavity to cavity interchangeability – a new mold making innovation.

1950’s
1952: Mr. Carlson opens Pacific Molds in El Monte, CA.
1956: Ontario Molds, another Carlson company is founded.
1958: First Multi-Material molds are designed and developed.
1959: Caco, Pacific and Ontario mold shops are consolidated under Caco-Pacific, Inc. in Covina, CA. The first Caco-Pacific multi-cavity (32) hot runner injection mold (which increased productivity by 107% over previous cold runner molds) is built.

1960’s
1961: Profit Sharing Plan is started.
1963: Caco-Pacific pioneers multi-cavity stack-mold technology for Polaroid film packs with total interchangeability of mold components. Gillette becomes a customer, beginning a major long term relationship to produce multi-cavity molds for razor handles, blade cartridges, dispensers, etc. that endures to this day.
1965: Caco-Pacific, Inc. develops multi-color/multi-shot molds for Amerace Corporation’s newly patented Chrome Plating of Plastics Technology.
1966: 14,000 sq. ft. of manufacturing space is added to increase capacity. Caco-Pacific perfects and supplies chrome-plated multi-colored dashboard knobs for the American Automobile Industry.
1967: Amerace Corporation buys Caco-Pacific, Inc. from Gil Carlson, which is now known as Caco-Pacific Division of Amerace. Gil Carlson remains President until his retirement in 1982.

1970’s
1970: 11,900 sq. ft. is added for mold testing and warehousing.
1973: Caco-Pacific assists MCA (Universal Studios) in development of world’s first Laser Optical Disc technology.
1976: Caco-Pacific supplies two-color key button injection molds for Apple’s first personal computer, the Apple I.
1977: Development and production of injection molds to produce Two and Three Color key buttons for IBM Electric Typewriters. Caco-Pacific also supplies Qume/Diablo with precision molds for Daisy Wheel printer technology.
1979: Caco-Pacific develops first Compact Disc (CD) injection mold tooling and assists General Electric and Dow Chemical to perfect the mold-ability of Laser Optical Discs.


1980’s
1981: 7,400 sq. ft. of engineering/general office space is added.
1984: Caco-Pacific designs and develops fastest cycling injection molds for 3M Corporation to mold thin-wall VHS Video Cassettes.
1985: Management buys company back from Amerace Corporation. The Profit Sharing Plan now owns 10% of the company. Under the new name of CACO PACIFIC Corporation, management invests considerable millions of dollars from 1985 to 1995 in sophisticated manufacturing equipment and automated machinery. Molds for multi-material parts become a large segment of CACO PACIFIC business.
1985 – 1989: During this period, CACO PACIFIC designs and develops hot runner injection molds for powdered metal and ceramic materials applications and for magnetic media cassettes with molded-in windows.


1990’s
1991: 401k Plan is added as a benefit to employees.
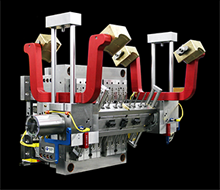
1993: The first servo electrically driven high-speed Mold Rotating Plate (MRP) is sold, cutting mold rotation time for fast shot-to-shot sequencing. Product line expands to include MRP-500, MRP-750 and MRP-1000.
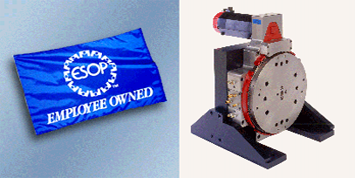
1994: With the retirement of a major shareholder of CACO PACIFIC, management decides to convert the Profit Sharing Plan to an Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) and contribute the shares being sold by the retiree to the ESOP. At this point the ESOP Trust owns approximately 50% of CACO PACIFIC.
1995 – 1996: CACO PACIFIC designs and builds its largest tooling project for Eastman Kodak to fill a complete new molding plant with multi-cavity hot runner molds. The project consisted of over 40 high cavitation molds for 6 different assembled plastic parts.
1996: CACO PACIFIC celebrates its 50 Year Anniversary (1946 – 1996). We calculate that we have graduated over 250 mold maker machinists from our rigorous 4-year Apprenticeship Program.
1998: Lobby expansion and 1,200 sq. ft. of additional office space completed to Corporate Headquarters in Covina.
1998 – 2001: CACO PACIFIC designs and builds its largest and fastest delivery tooling project for Gillette, consisting of over 60 mold systems to produce three different parts (including hot runners, mold bases and MRPs), that rolled out fully assembled and tested at a rate of one every two weeks.
1999: The Interactive Process Manager (IPM) is unveiled, which enables “intelligent” molds and Mold Rotating Plates (MRPs).
1999: Electrode palletizing is expanded and management invests heavily into automated robotic equipment to enhance our delivery speed to our customers.


2000’s
2000: LIT (Low Inertia Turning) is introduced as a new multi-shot technology.
2000: ISO 9001 certification is awarded to CACO PACIFIC. Our certification has been renewed in 2021.
2001: CACO Technologies, Inc., a division of CACO PACIFIC Corporation, Covina, is created to market our line of Bolt-On Hot Runner Systems, Mold Rotating Plates (MRP) and Interactive Mold Mounted Controllers (IPM).
2002 – 2003: Development of LIT Individual Core Rotation and LIT CUBE technologies.
2004: Another major shareholder of CACO PACIFIC retires and management again contributes the shares to the ESOP, increasing to 60% employee ownership through the ESOP Trust.
2004 – 2007: Major investments are made in CNC High Speed Hard Milling, CNC High Speed Hard Turning and CNC Surface Grinding equipment.
2009: CACO PACIFIC becomes 100% employee owned when the last owner outside the ESOP sells his shares back to the company. The ESOP Trust owns 100% of CACO PACIFIC.
2010: More major investments are made in nearly doubling the capacity of our pre-heat treat CNC Milling operations.
2012: MAPP (Multiple Alternating Product Positions) is introduced as a new technology for movement of parts in multi-shot molding.
2013: Individual Valve Pin Shut Off in a Common Actuation Plate is developed.
2013: Recognizing a need for increased capacity in grinding round components, CACO PACIFIC expands and upgrades the ID/OD grinding department and purchases new equipment, including a new CNC ID/OD Grinder.